Stevia has gained popularity as a “natural” sweetener that offers a zero-calorie alternative to sugar. However, the reality behind this widely used sweetener may not be as innocent as it seems. Many consumers are unaware of the industrial processes involved in producing commercial stevia, as well as the potential health risks associated with its consumption. This article aims to reveal the truth about stevia and why it may not be the ideal sweetener that many believe it to be.
Key Takeaways
- Commercial stevia is highly processed and chemically extracted.
- Stevia may trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- This sweetener can lead to heart rhythm issues and gut microbiome disruption.
- Natural sweeteners like raw honey provide health benefits without the risks.
The Processing of Stevia: A Closer Look
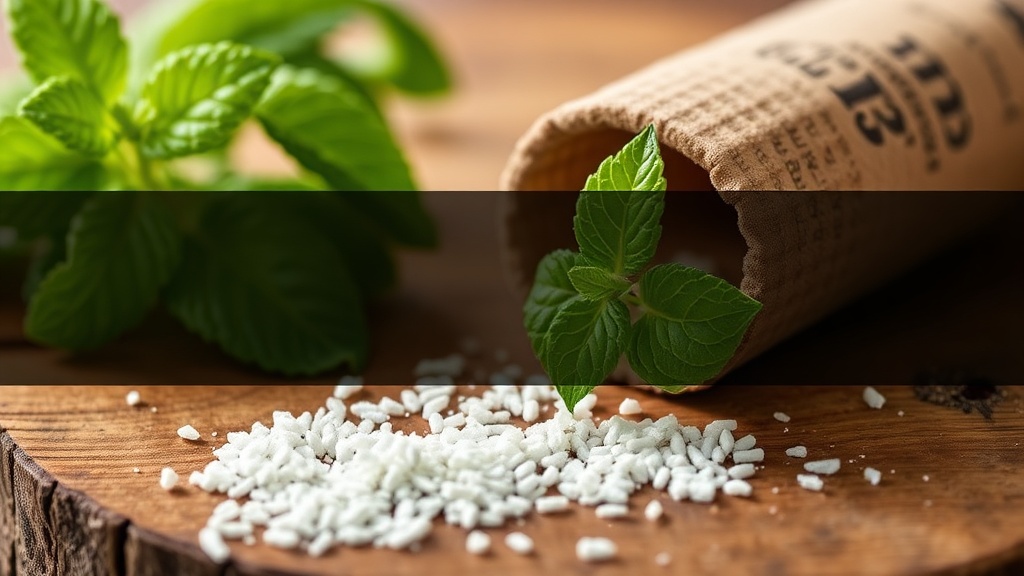
At first glance, stevia appears to be a harmless plant-based sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. However, the truth is that the stevia products found in grocery stores undergo extensive industrial processing. Manufacturers extract sweet compounds known as steviol glycosides using chemical solvents, resins, and filtration methods. This results in a white powder or liquid that bears little resemblance to the original plant.
Despite the labeling of stevia as “natural,” the extraction process strips away the wholesome qualities of the plant. The body may not recognize these isolated compounds as it does with whole foods, potentially leading to unexpected health consequences. The claim of being a natural sweetener becomes questionable when you consider the extensive processing involved.
Furthermore, many commercial stevia products contain additives and fillers that can further complicate their health implications. As consumers, it’s essential to be aware of what we’re putting into our bodies, especially when the marketing claims can be misleading.
Allergic Reactions Linked to Stevia
One of the significant concerns surrounding stevia is its potential to cause allergic reactions. Being part of the ragweed family (Asteraceae), individuals who are sensitive to ragweed may also react to stevia. Research indicates that nearly 45% of the population may have some level of sensitivity to this plant family, leading to symptoms such as skin rashes, headaches, or digestive discomfort.
While not everyone may experience these allergic reactions, it is crucial for consumers to be aware that a “healthy” sweetener could be responsible for triggering immune responses. The presence of stevia in various foods and drinks could pose risks to individuals with allergies, highlighting the need for caution and awareness.
Moreover, the hidden nature of these reactions can make it difficult for individuals to pinpoint the cause of their discomfort, leading to confusion and frustration. As stevia becomes more prevalent in our diets, understanding these potential risks is vital for informed choices.
Cardiac Concerns: The Impact of Stevia
Stevia has also been associated with heart rhythm disturbances, particularly in sensitive individuals. Reports suggest that consuming stevia may double the risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and other cardiac irregularities. While some individuals may use stevia daily without experiencing symptoms, others have reported noticeable heart palpitations or skipped beats following consumption.
The heart’s electrical system is delicate, and the chemical compounds found in processed stevia can exert mild stimulatory effects. For those predisposed to heart issues, even minor disturbances can accumulate over time, potentially leading to more significant health problems.
This connection between stevia and heart health raises critical questions about its safety as a sweetener. Given the increasing prevalence of heart-related conditions, consumers must consider the implications of stevia on their cardiovascular health.
Gut Health and Stevia: What You Should Know
Research has indicated that stevia can disrupt the gut microbiome, which is essential for digestion, immunity, and even mental health. The balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut can be altered by the consumption of artificial or processed sweeteners, including those labeled as “natural.” This disruption can lead to inflammation, digestive issues, and conditions like leaky gut syndrome over time.
Moreover, some studies suggest that stevia may negatively affect the endothelial lining of blood vessels, potentially leading to long-term vascular damage. This could further impair nutrient absorption and contribute to an array of health issues.
The connection between gut health and overall well-being cannot be overstated. As such, the potential impact of stevia on the gut microbiome is a significant concern for individuals seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Natural Sweetener Alternatives
If you’re looking for a sweetener that aligns more closely with natural sources, consider alternatives like raw honey. Raw honey is rich in enzymes, minerals, and trace nutrients, offering sweetness alongside various health benefits, including antimicrobial properties. It’s essential to use honey in moderation, but choosing raw, unfiltered varieties can provide a wholesome sweetening option without the risks associated with processed sweeteners.
Other natural sweeteners include maple syrup and coconut sugar, which offer more nutritional benefits compared to highly processed options. By opting for whole-food sweeteners, consumers can enjoy sweetness without compromising their health.
In summary, while stevia may be marketed as a healthy alternative to sugar, understanding its processing, potential health risks, and available natural alternatives is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is stevia, and how is it made?
Stevia is a natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. The sweet compounds, known as steviol glycosides, are extracted through industrial processes involving chemical solvents and filtration methods. This results in a highly refined product that is often marketed as “natural,” but the processing involved raises questions about its health implications.
- Can stevia cause allergic reactions?
Yes, stevia can trigger allergic reactions, particularly in individuals sensitive to the ragweed family. Symptoms may include skin rashes, headaches, nasal congestion, and digestive discomfort. Awareness of these potential reactions is essential for those who are prone to allergies.
- Does stevia affect heart health?
Some studies suggest that stevia may be linked to heart rhythm disturbances, such as atrial fibrillation and palpitations. While not everyone experiences these effects, sensitive individuals should exercise caution when consuming stevia, especially if they have pre-existing heart conditions.
- How does stevia impact gut health?
Research indicates that stevia can disrupt the gut microbiome, favoring harmful bacteria over beneficial strains. This imbalance may lead to digestive issues and inflammation over time, highlighting the importance of considering gut health when choosing sweeteners.
- What are some healthier alternatives to stevia?
Healthier alternatives to stevia include natural sweeteners like raw honey, maple syrup, and coconut sugar. These options provide sweetness along with nutritional benefits, making them more suitable choices for those seeking to avoid processed sweeteners.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while stevia may be presented as a natural and healthy sweetener, a closer examination reveals several concerns regarding its processing, potential allergic reactions, impacts on heart health, and effects on gut microbiome balance. Consumers should be cautious and informed about their sweetener choices. Embracing whole-food alternatives like raw honey can help ensure that you enjoy sweetness without the associated risks of heavily processed sweeteners such as stevia.